Trajectory Record
The Trajectory Record Node offers a real-time teaching functionality, currently supported only for robotic arm hardware. This feature can be used within a Graph as well as directly via the robotic arm's quick action controls. Trajectories recorded can be played or paused in a full-screen virtual environment.
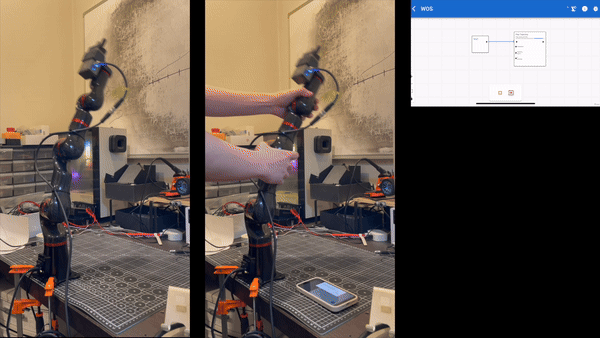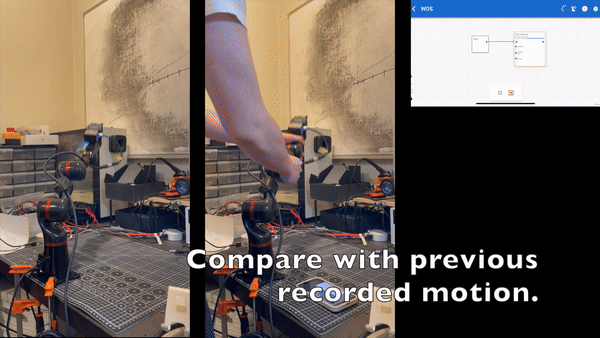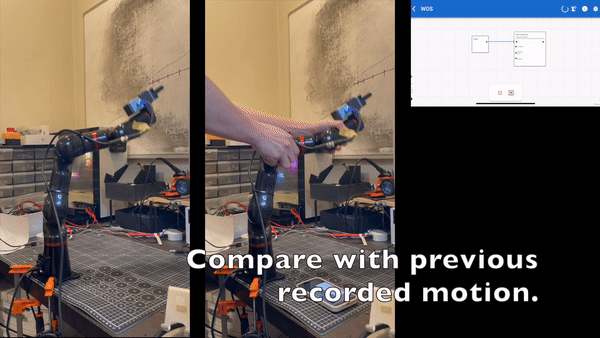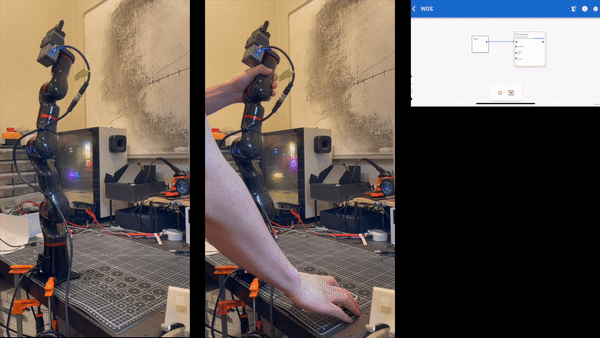
Setting Up the Trajectory Record Node
Let's take the STR400 as an example:
-
Initial Setup:
- Ensure you have an STR400 robot setup.
- In the robotic arm's quick action control panel, select the Manual mode under the Action Tab.
-
Manual Mode Caution:
- In Manual mode, the STR400's joints become passive, meaning they operate without active torque. It's essential to manually support the robot arm to prevent it from collapsing.
-
Recording a Trajectory:
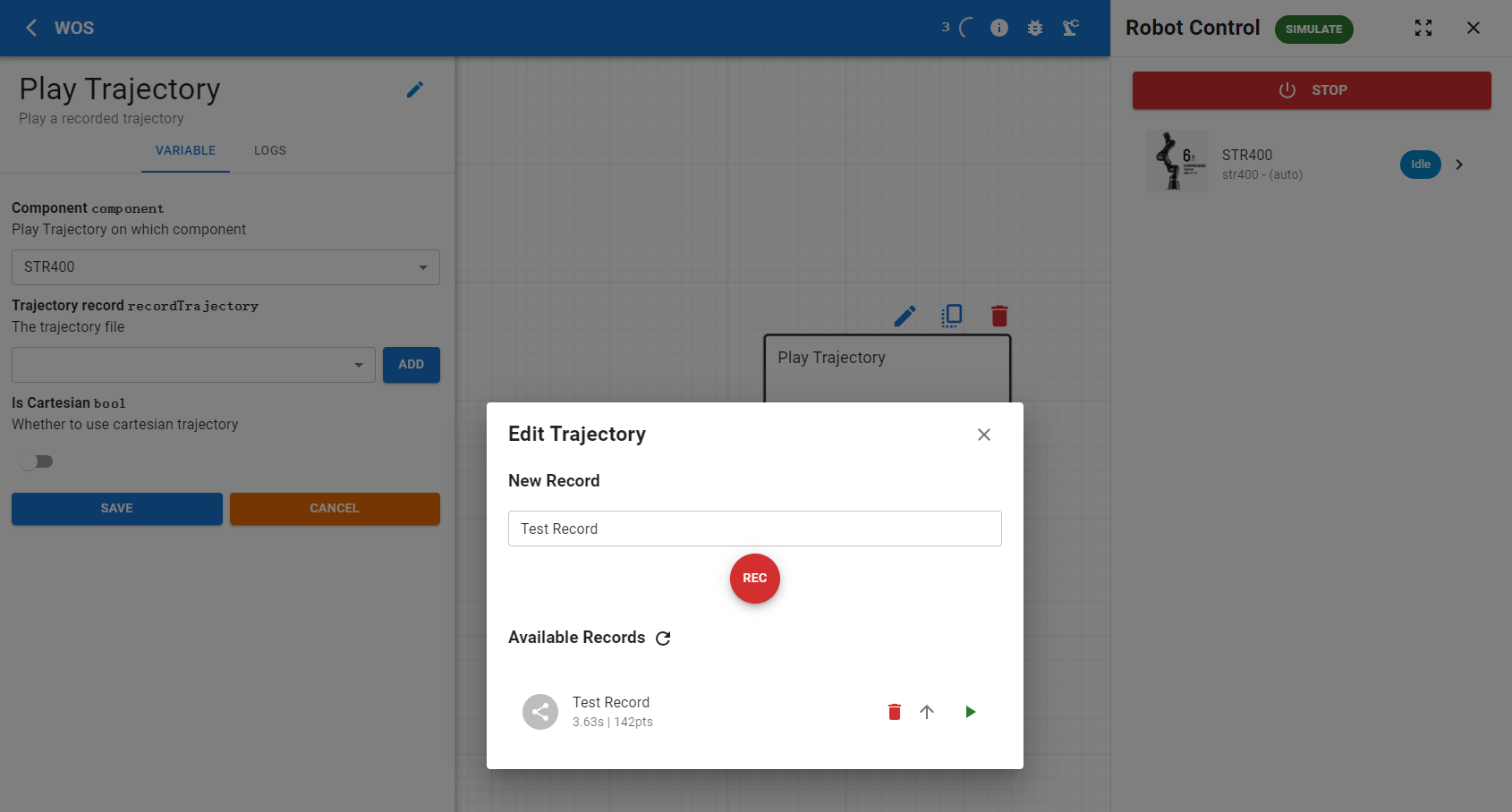
- Open the Trajectory Node Editor and select the STR400 as the component.
- Click on
ADDunder the Trajectory Record section to bring up a dialog box where you can create a new trajectory record and view all previously recorded trajectories within the system.
-
Start Recording:
- Press the
RECbutton to begin recording. At this point, manually manipulate the robotic arm; every subtle movement will be captured. - After completing the recording, click the
SAVEbutton to save the trajectory. The node is now ready for use.
- Press the
Playback Precautions
- Before playing back any trajectory, the system will perform a slow
Move Jointsoperation to position the arm at the starting point of the trajectory. - It is advisable to first use simulation mode to check if the arm's movements meet expectations before playing it back on the actual hardware.
Recommendations
- Simulation First: Always verify the trajectory in simulation mode to ensure it operates as expected without causing any unexpected movements or errors.
- Supervision: When operating in manual mode, ensure constant supervision and physical support to prevent any damage due to the lack of active torque in the joints.
This functionality enhances the flexibility and applicability of the WOS system, allowing users to precisely teach and record complex movements directly through hands-on interaction with the robotic arm.